With ACLED’s expansion to Central Asia and the Caucasus, Afghanistan will now be covered as part of this region alongside Georgia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, and Tajikistan. For updates on South and Southeast Asia, please see the new individual South Asia Regional Overview and Southeast Asia Regional Overview.
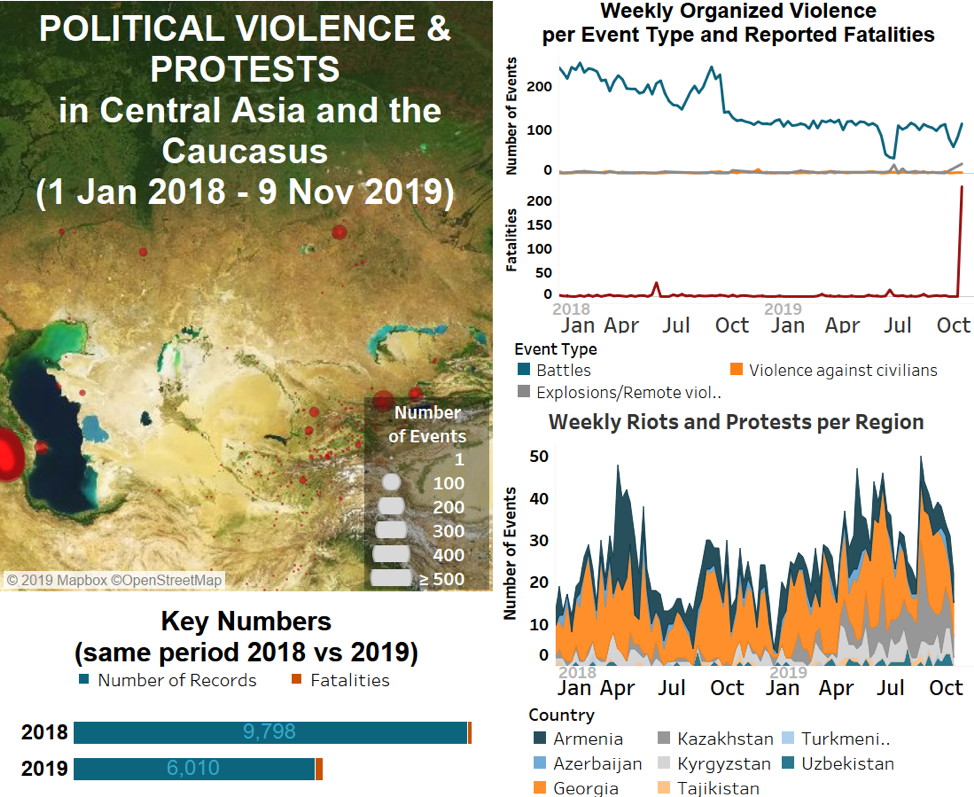
During the past week, the Islamic State conducted attacks on the Tajikistan border and in Afghanistan; meanwhile, in the Caucasus, ceasefire violations continued along the Armenia-Azerbaijan border. In Georgia, far-right extremist groups continued targeting civilians with increased cases of violence.
In Afghanistan, fighting between different warring factions continued over the last week. Government forces clashed with both the Taliban and Islamic State (IS) fighters in several provinces, with the highest number of events reported in the provinces of Helmand, Ghazni, Kandahar and Zabul. Furthermore, IS militants attacked Taliban forces in Nangarhar province, causing several reported fatalities and injuries. Referring to itself as Islamic State Khorasan (IS-K), the Afghan affiliate of IS emerged in 2015 with the aim of expanding into Khorasan, a historical region that included parts of present-day Iran, Central Asia, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. The group’s stronghold remains in eastern Afghanistan, particularly the province of Nangarhar, though it has also carried out major attacks in other parts of Afghanistan and in neighboring Pakistan.
During the past week, an attack on a military checkpoint in Tajikistan on 6 November was also reportedly carried out by assailants affiliated with the IS-K, some of whom crossed into Tajikistan from neighboring Afghanistan (RFE/RL, 10 November 2019). The twenty militants, believed to be Tajik nationals, launched the attack on the Ishqobod frontier post on the border with Uzbekistan, 50km southwest of Tajikistan’s capital, Dushanbe. The attack reportedly killed a border guard and a police officer; the militants lost 15 fighters in the ensuing firefight. The attack in Tajikistan raises concern about the growth of the Afghan IS affiliate and its longstanding aim to spread from its enclave in Afghanistan (New York Times, 06 November 2019). Afghanistan and Tajikistan share a long border of over 1300km, and in recent years both Tajik and foreign authorities, including US and Russian officials, have been warning about the threat of IS expansion into Tajikistan.
Meanwhile, in Azerbaijan and Armenia, ceasefire violations remained similar to the previous week, with 49 armed clashes along the Artsakh-Azerbaijan line, most intensively in Agdam, Khojavend, and Tartar regions in eastern Azerbaijan. Thirty armed clashes along the Armenia-Azerbaijan line of contact were reported, which is slightly higher than in the previous week.
In Georgia, the far-right group Georgian March, after a relatively long absence, tried to block the premier of an internationally acclaimed movie telling the love story of two male dancers in Georgia’s national ballet ensemble. The group denounced it as ‘gay propaganda,’ similar to the statements of the Georgian church that claimed the movie was conflicting with traditional Georgian values. The demonstrators of the extremist group were reported to attack moviegoers in Batumi and Tbilisi. In one case, head trauma was reported by a moviegoer, who is also known to be a civil rights activist. Intervening police forces detained over two dozen rioters, but similar demonstrations continued throughout the week requiring heavy police presence in the cinemas of Tbilisi and Batumi.
© 2019 Armed Conflict Location & Event Data Project (ACLED). All rights reserved.