Last updated: 26 June 2025
Amid the ongoing war in Ukraine, this aerial photograph shows the destruction in the village of Bohorodychne in the Donetsk region on 27 January 2024. Photo by Roman Pilipey/AFP via Getty Images
ACLED’s Ukraine Conflict Monitor provides near real-time information on the ongoing war, including an interactive map of the latest data from the start of Russia’s invasion, a curated data file, and weekly situation updates. It is designed to help researchers, policymakers, media, and the wider public track key conflict developments in Ukraine. It is released every Wednesday, with data covering events from Saturday to Friday of the preceding week and providing updates to past events as new or better information becomes available.
Ukraine war situation update
14 June – 20 June 2025
Key trends
- In the Donetsk region, Russian forces seized two villages north and northwest of Velyka Novosilka and continued advancing around Pokrovsk and south of Kostiantynivka.
- Russian forces seized one settlement near the international border north of Sumy city.
- ACLED records at least 30 Russian long-range missile and drone strikes, over a third of them in Kyiv city and the surrounding region.
- Russian shelling, missiles, and drones killed at least 44 civilians in the Dnipropetrovsk, Donetsk, Kharkiv, Kherson, Odesa, and Sumy regions, as well as in the city of Kyiv. Additionally, Ukrainian drones reportedly killed at least four civilians in the occupied parts of the Donetsk, Kherson, and Luhansk regions.
Key events
- 16 Jun. | Kyiv – Russia returns the bodies of more than 6,000 Ukrainian soldiers
- 17 Jun. | Odesa – Russian drones hit Odesa city center, killing two civilians and wounding 26
- 18 Jun. | Zaporizhia – Ukraine’s intelligence services shoot dead a Ukrainian politician who joined the Russian government in occupied Berdiansk
Spotlight: Russia launches one of the deadliest strikes on Kyiv city
Overnight on 17 June, Russia launched 16 missiles and 175 drones on Kyiv city,1Yuliia Abramova, “The number of victims of the Russian strike on a residential building increased in Kyiv — State Emergency Service (photo),” TSN, 17 June 2025 (Ukrainian) killing 28 civilians and wounding over 140. ACLED records casualties and damage to civilian infrastructure in seven out of 10 of Kyiv’s districts. This includes substantial damage to over 50 residential houses, as well as several educational institutions, non-residential buildings, and railway infrastructure.2BBC News, “A high-rise building destroyed in Kyiv by a Russian strike – many dead and injured, people are under the rubble,” 17 June 2025 (Ukrainian) One of the missiles collapsed a nine-story apartment building in the Solomyanskyi district of the city. Over 400 emergency workers spent two days on recovery work, retrieving the bodies of 23 civilians from under the rubble.3Facebook @State Emergency Service of Ukraine, 19 June 2025 (Ukrainian) In the Darnytskyi district, a Russian drone flew into a high-rise residential building, damaging several floors and killing three civilians. Local authorities also reported finding remains of cluster munitions in the Shevchenkivskyi district.4Radio Free Europe, “Kyiv authorities warn of explosive debris, cluster munitions after Russian strike,” 17 June 2025 (Ukrainian)
Further strikes were also recorded in the surrounding Kyiv region, where a civilian was wounded, and several private houses and other infrastructure were damaged in four separate districts.
The 17 June attack was the deadliest attack on Kyiv city after the strikes on 8 July 2024 and 29 December 2023 that claimed the lives of 34 and 32 people, respectively. More recently, on 24 April 2025, Russian drones and missiles killed 13 and wounded 90 civilians across the city. The frequency of Russian attacks on Kyiv city and the eponymous region has been on the rise since mid-May.
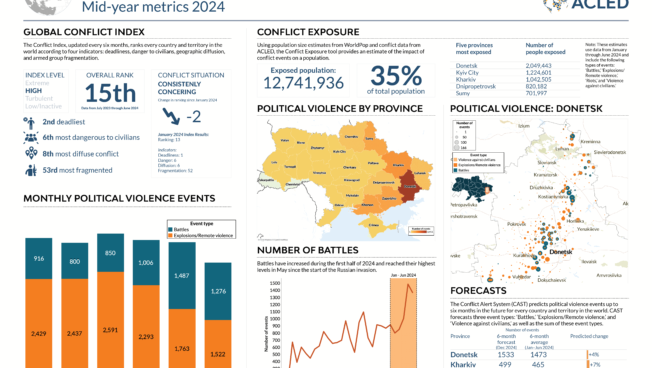
Explore the ACLED Conflict Exposure tool to assess the numbers of people affected by armed violence, disaggregated by locations, time period, and actors involved.
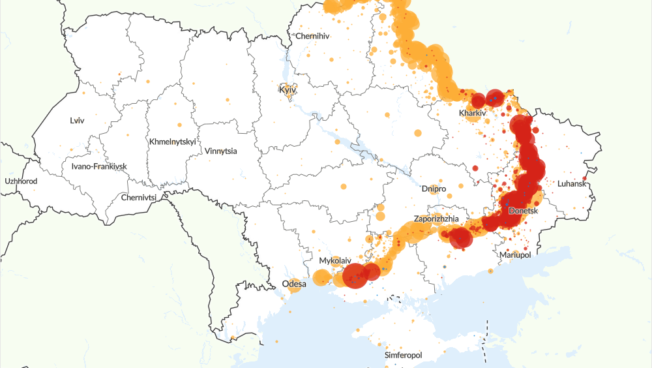
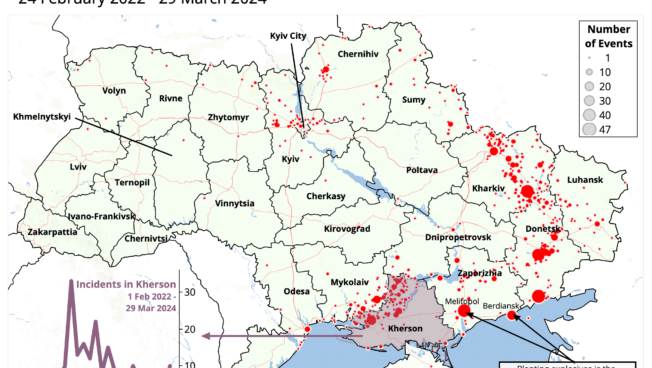
Ukraine Conflict: Interactive Map
This interactive map includes political violence events in Ukraine since the start of the Russian invasion on 24 February 2022.
Date and subset filters
By default, the map displays data for the most recent week. Use the date filters to change the date range in view.
Use the subset filters to analyze trends in more detail.
Changing view
By default, the map is set to event view, which uses scaled circles to show events at a given location. Click on a region in Ukraine to zoom in for a more detailed view. Hovering over a region will give a count of events within its borders.
Changing to region (oblast) view will switch the map to a choropleth, giving an overview of event density per region. This will also disable the zoom function.
Events in Russia
While in event view, use the ‘Events in Russia’ toggle to show or hide conflict-related events in Russia. Conflict-related events are identified as follows:
- All events with the ‘Battles’ or ‘Explosions/remote violence’ event type.
- Events with the ‘Violence against civilians’ event type, where the actor is:
- Ukrainian or Russian military
- Russian border guards
- Pro-Ukrainian Russian militias
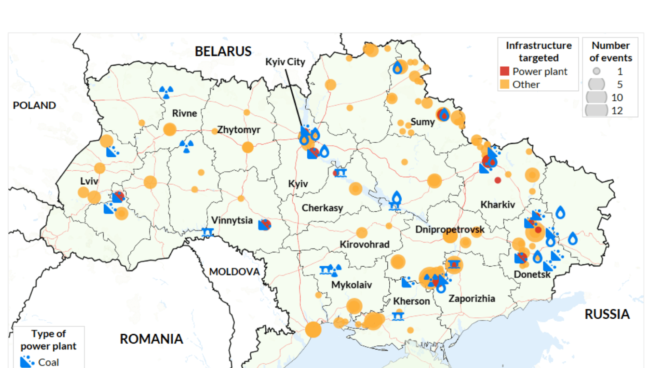
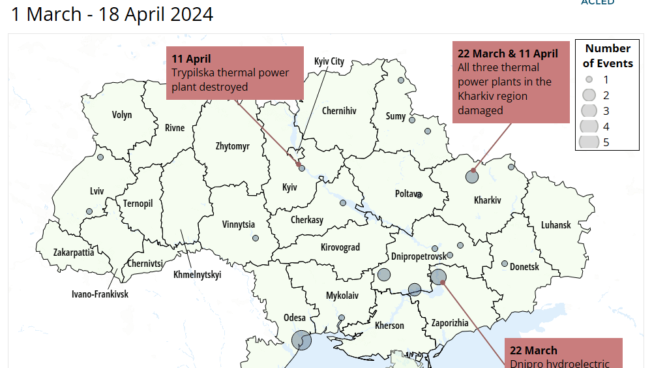
Attacks on Ukranian infrastructure
ACLED uses four automatically generated infrastructure tags when coding events that occur in Ukraine, each covering a vital sector that focuses on civilian infrastructure: energy, health, education, and residential infrastructure.
For more information, read our methodology explainer.
Event counts and civilian fatalities
The box in the bottom right hand corner displays event counts in total, disaggregated by event type, and filtered by date or subset according to the options already selected.
It also shows a conservative estimate of civilian fatalities, limited to events where civilians are targeted directly. Military casualties are not represented on the map as they are largely unverifiable.
For more information on how ACLED codes fatalities, read our methodology explainer.
Curated Data
This file contains all political violence events, demonstration events, and strategic developments recorded in Ukraine and the Black Sea from the beginning of ACLED coverage in 2018 to the present.
For an overview, see our interactive dashboard.
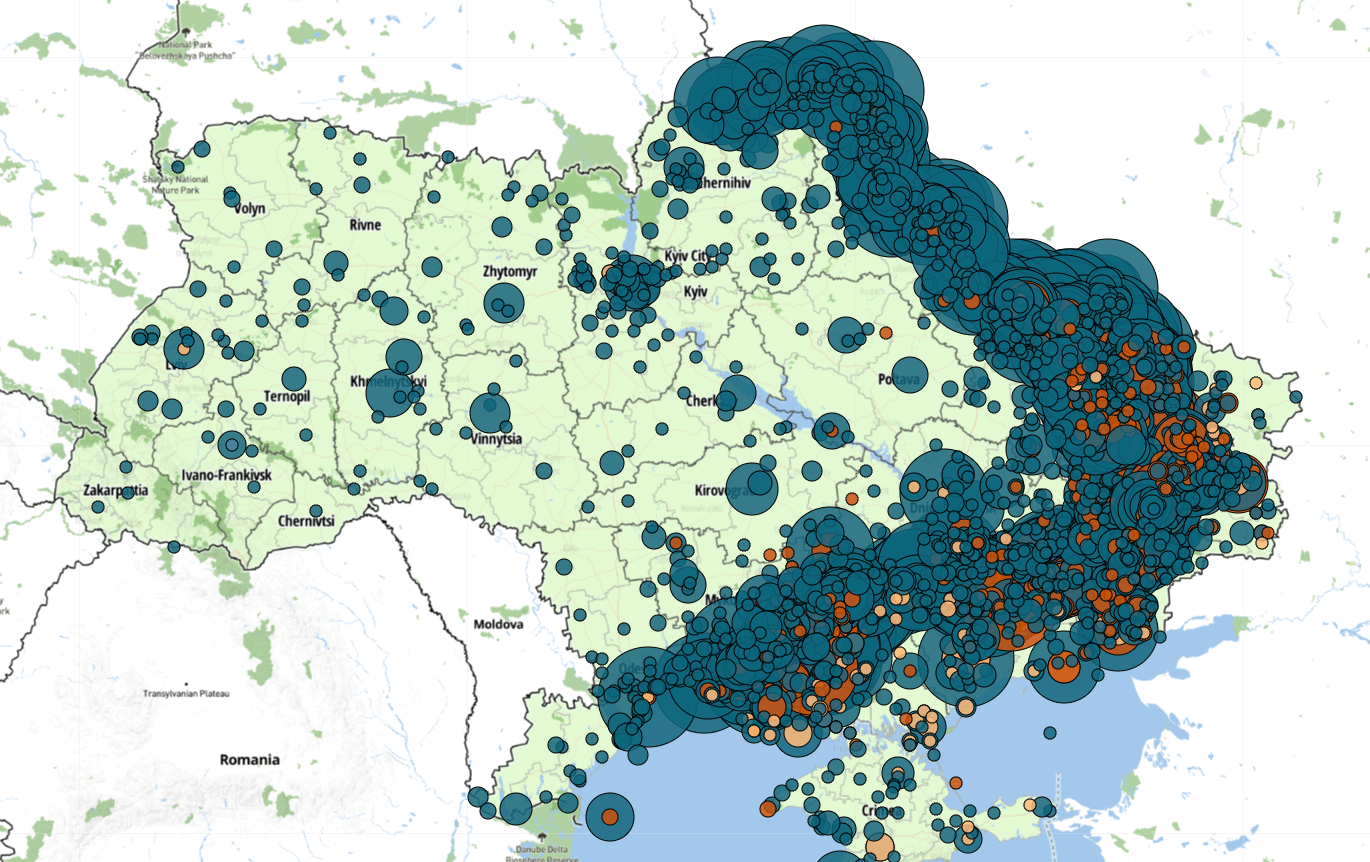
Ukraine & the Black Sea ( 13 June 2025 )
Attacks on Ukranian infrastructure
ACLED uses four automatically generated infrastructure tags when coding events that occur in Ukraine, each covering a vital sector that focuses on civilian infrastructure: energy, health, education, and residential infrastructure. This file contains all events featuring one or more of these tags.
For more information, read our methodology note.
Sign up for Ukraine Conflict Monitor updates
Information & Analysis
For additional information on the conflict in Ukraine, check our analysis of political violence trends from the start of ACLED coverage in 2018.